How to Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Without Breaking the Bank
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is an essential strategy for startups and businesses to validate their ideas while minimizing costs and risks.
Varritech
March 11, 2025
How to Build a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) Without Breaking the Bank
Building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is an essential strategy for startups and businesses to validate their ideas while minimizing costs and risks. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating an MVP without overspending.
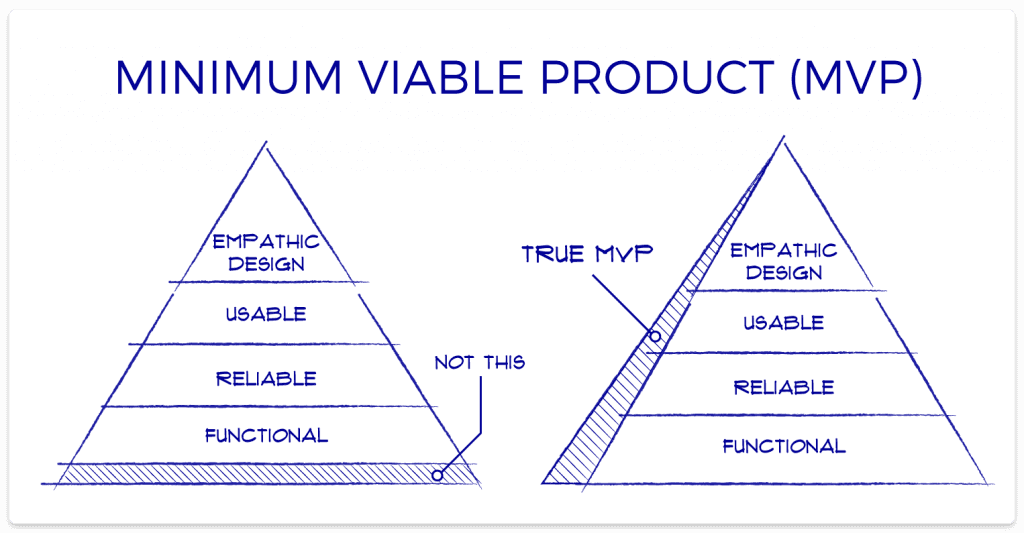
1. Understand What an MVP Is
An MVP is a simplified version of your product that includes only the core features necessary to address the primary problem for your target audience. It allows you to:
Test your product idea with minimal resources.
Gather real-world feedback from early adopters.
2. Steps to Build an MVP on a Budget
a. Define the Problem
Clearly identify the problem your product will solve. This ensures you focus only on features that address this issue directly24.
b. Conduct Market Research
Validate your idea by researching your target audience and competitors. This helps you understand market demand and identify gaps13.
c. Prioritize Core Features
Use prioritization frameworks like the MoSCoW method (Must-have, Should-have, Could-have, Won’t-have) to determine which features are essential for the MVP24.
d. Create a Prototype
Develop a simple prototype or wireframe to visualize the user journey and core functionality. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD can help you design cost-effectively67.
e. Leverage Low-Cost Development Options
Use no-code/low-code platforms (e.g., Webflow, Bubble) to build your MVP quickly and affordably.
Outsource development to freelancers or small agencies if coding is required67.
f. Launch Quickly and Collect Feedback
Release the MVP to a limited audience and observe their interactions. Focus on gathering actionable insights rather than perfecting the product14.
3. Cost-Saving Tips
Start Small: Begin with a single feature that solves the primary pain point.
Use Existing Tools: Utilize pre-built templates, open-source software, or APIs to save time and money.
Test Using Smoke Tests: Create landing pages or ads to gauge interest before building the full product46.
Iterate Based on Feedback: Use customer insights to refine your product incrementally, avoiding large-scale redesigns35.
4. Real-Life Examples of Budget-Friendly MVPs
Dropbox started with a simple explainer video demonstrating its concept.
Twitter began as "twttr," focusing solely on short messaging functionality.
Amazon launched as an online bookstore before expanding into other categories6.
5. The Build-Measure-Learn Cycle
Adopt the Lean Startup methodology:
Build: Develop the MVP with essential features.
Measure: Analyze user feedback and data.
By following these steps, you can create an MVP that validates your idea while keeping costs under control, setting the foundation for future growth and success.